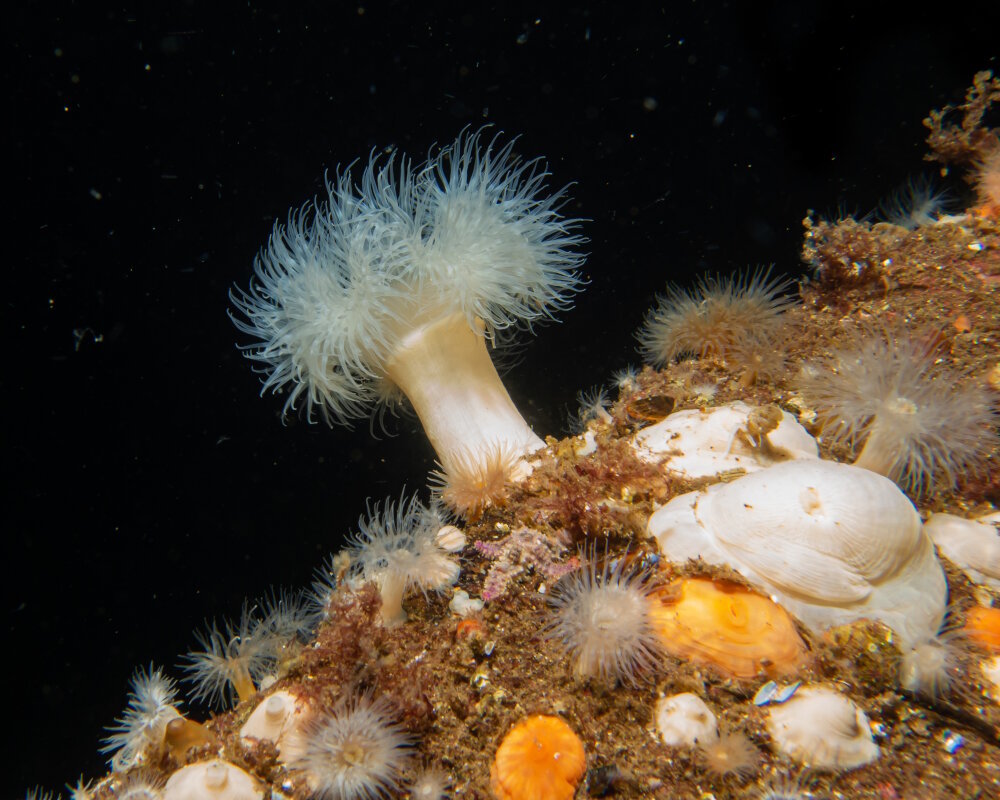
Sealife guideThe plumose sea anemoneMetridium senile
Last updated on 03/25/2025 at 09:49 PM
Taxonomy
- Common name: Plumose sea anemone, plumose anemone, frilled sea anemone, plumose sea anemone, cloned plumose anemone, clonal plumose anemone, brown sea anemone
- French name: Oeillet de mer ou anémone plumeuse, anémone plumeuse, actinie plumeuse
- Scientific name: Metridium senile (Linnaeus, 1761)
- Family name: Metridiidae
- Order name: Actiniaria
- Class name: The anthozoans [Anthozoa]
Description
The plumose sea anemone has a cylindrical body with a broad base that allows it to anchor firmly to various surfaces. Its numerous, slender tentacles form a dense crown when fully extended. Individuals can grow up to 12 inches in height. This species displays a wide range of colors, including white, orange, dark green, brown, gray, red and yellow.
Geographic range
The plumose sea anemone is a circumboreal sea anemone found in the cold waters of the North Atlantic, North Pacific and Arctic oceans.
Habitat
The plumose sea anemone thrives in diverse marine environments, including rocky reefs, sandy seabeds and even artificial structures such as ship hulls and harbor docks, showcasing its impressive adaptability. It can be found from the intertidal zone to depths of several hundred meters.
Diet
As a sessile predator, the plumose sea anemone primarily feeds on plankton and suspended organic particles. Its tentacles contain specialized stinging cells called cnidocytes, which allow it to capture and immobilize prey before ingestion. This anemone also plays a crucial ecological role by filtering water and providing shelter for various marine species.
Reproduction
The plumose sea anemone employs both sexual and asexual reproduction strategies. In sexual reproduction, individuals release their gametes into the water, producing planktonic larvae that eventually settle and transform into adult anemones. Asexual reproduction occurs through budding or binary fission, enabling the species to rapidly multiply and colonize new habitats.
Did you know ?
The plumose sea anemone is of particular interest in marine biology and benthic invertebrate ecology due to its diverse morphology and adaptability. Research on this species focuses on its color variations, which provide insights into population dynamics, as well as its defense mechanisms involving the production of toxic substances.
Discover also

Atlantic sea nettle
(Chrysaora quinquecirrha)

Big siphonophore
(Forskalia edwardsii)

Blue jellyfish
(Cyanea lamarckii)

Elkhorn coral
(Acropora palmata)

Labyrinthine brain coral
(Diploria labyrinthiformis)

Portuguese man-o-war
(Physalia physalis)

Staghorn coral
(Acropora cervicornis)

Yellow encrusting sea anemone
(Parazoanthus axinellae)
The marine species from north Atlantic ocean

Banded cleaner shrimp
(Stenopus hispidus)

Bandtail puffer
(Sphoeroides spengleri)

Blackbar soldierfish
(Myripristis jacobus)

Giant caribbean anemone
(Condylactis gigantea)

Hawksbill sea turtle
(Eretmochelys imbricata)

Kemp's ridley sea turtle
(Lepidochelys kempii)
Queen angelfish
(Holacanthus ciliaris)

Yellowtail snapper
(Ocyurus chrysurus)
Les destinations de plongée

A stop in Barcelona

A visit to the Getty Center

A walk down Ocean Drive

Aquatica water park
Dive centers

'Les Ilets' dive center

Noa dive center

Sea Dwellers Dive Center






























