Sealife guideSharks: guardians of the oceanMarine vertebrates
Last updated on 02/05/2026 at 10:36 PM
Sharks, like rays, belong to the class of chondrichthyans, which includes all cartilaginous fish. Within this class, sharks are part of the subclass of elasmobranchs.
Classification
Sharks are classified into eight orders, mainly according to the shape and arrangement of their different fins:
- the order Carcharhiniformes29 species
- the order Heterodontiformes4 species
- the order Hexanchiformes2 species
- the order Lamniformes6 species
- the order Orectolobiformes11 species
- the order Pristiophoriformes0 species
- the order Squaliformes3 species
- the order Squatiniformes2 species
Explore the sharks of the order Carcharhiniformes, the largest shark group, characterized by their nictitating membranes, diverse sizes and varied diets ranging from small fish to marine mammals.

Coral catshark
(Atelomycterus marmoratus)
(Atelomycterus marmoratus)

Dark shyshark
(Haploblepharus pictus)
(Haploblepharus pictus)

Leopard catshark
(Poroderma pantherinum)
(Poroderma pantherinum)

Silky Shark
(Carcharhinus falciformis)
(Carcharhinus falciformis)
Explore the sharks of the order Heterodontiformes, known for their distinctive blunt heads and unique teeth, which help them crush hard-shelled prey like sea urchins and mollusks.

Crested hornshark
(Heterodontus galeatus)
(Heterodontus galeatus)

Horn shark
(Heterodontus francisci)
(Heterodontus francisci)

Port Jackson shark
(Heterodontus portusjacksoni)
(Heterodontus portusjacksoni)

Zebra bullhead shark
(Heterodontus zebra)
(Heterodontus zebra)
Discover the sharks of the order Hexanchiformes, easily recognized by their six or seven gill slits, ancient lineage and deep-sea habitats.

Broadnose sevengill shark
(Notorynchus cepedianus)
(Notorynchus cepedianus)

Frilled shark
(Chlamydoselachus anguineus)
(Chlamydoselachus anguineus)
Explore the sharks of the order Lamniformes, known for their large size, powerful swimming and iconic species like the great white shark and the mako shark.

Basking Shark
(Cetorhinus maximus)
(Cetorhinus maximus)

Great white shark
(Carcharodon carcharias)
(Carcharodon carcharias)

Pelagic thresher shark
(Alopias pelagicus)
(Alopias pelagicus)

Short fin mako
(Isurus oxyrinchus)
(Isurus oxyrinchus)
Explore the sharks of the order Orectolobiformes, also called carpet sharks, including species like the whale shark and bamboo sharks, often found resting on the sea floor or camouflaged among reefs.

Brownbanded bamboo shark
(Chiloscyllium punctatum)
(Chiloscyllium punctatum)

Ornate wobbegong
(Orectolobus ornatus)
(Orectolobus ornatus)

Spotted wobbegong
(Orectolobus maculatus)
(Orectolobus maculatus)

Whale shark
(Rhincodon typus)
(Rhincodon typus)
Explore the sharks of the order Pristiophoriformes, also known as sawsharks, recognized by their long, toothed snouts used to detect and capture prey on the sea floor.
Explore the sharks of the order Squaliformes, commonly called dogfish sharks, which are generally small to medium-sized deep-sea sharks known for their spiny dorsal fins and discreet behavior.

Greenland shark
(Somniosus microcephalus)
(Somniosus microcephalus)

Leafscale gulper shark
(Centrophorus squamosus)
(Centrophorus squamosus)

Spiny dogfish
(Squalus acanthias)
(Squalus acanthias)
Explore the sharks of the order Squatiniformes, known as angel sharks, which have flattened bodies and broad pectoral fins, allowing them to lie camouflaged on the sea floor while waiting to ambush prey.

Common angelshark
(Squatina squatina)
(Squatina squatina)

Pacific angelshark
(Squatina californica)
(Squatina californica)
Description

Shark anatomy
Geographic range and habitat
Sharks are found in all the world's seas and oceans, across all latitudes and at all depths: from warm tropical waters to icy polar waters, from shallow waters along coasts and coral reefs to the deep sea !
Some shark species are pelagic, while others are benthic and live resting on the seafloor.
Diet
Most often resting during the day, sharks feed mainly at night, when they are most active in searching for prey.
Sharks are top predators at the apex of the marine ecosystem's food chain. Their diet is mainly carnivorous but highly varied: mollusks for nurse sharks, squid, octopuses, fish of all sizes, sea lions, seals and even plankton for the whale shark and the basking shark.
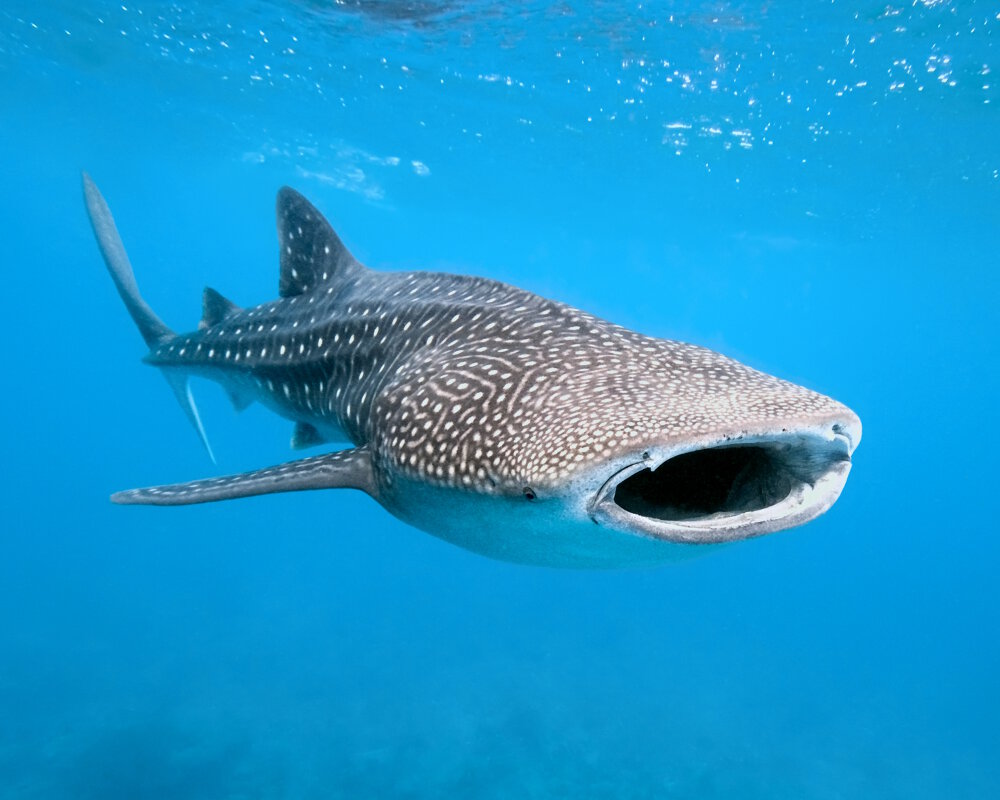

The whale shark feeds only on plankton ! © Krzysztof Odziomek | Dreamstime.com
To protect their eyes when attacking prey, some sharks like the great white shark can roll their eyes back, while others like the tiger shark have a very strong, semi-transparent nictitating membrane that covers their eyes like a third eyelid !
Reproduction
Typically in fish, fertilization is external after the release of male and female gametes into seawater. Sharks, however, are an exception to this rule and have internal fertilization. The male shark's pelvic fins have evolved into reproductive organs called claspers.
All sharks have internal fertilization, but the development and feeding of the embryo vary depending on the species. Some sharks are oviparous, others are ovoviviparous, the most common reproductive mode and a few are viviparous, such as the lemon shark.
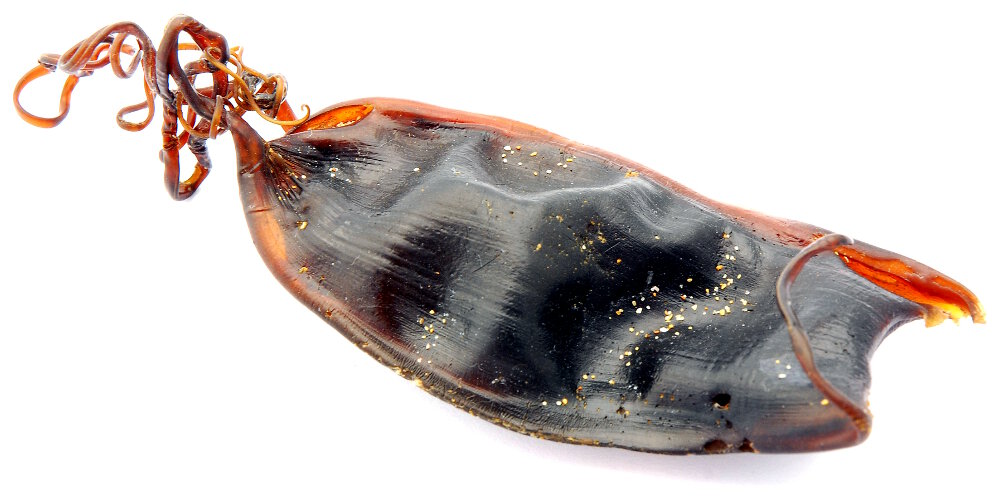

The capsule containing the shark egg is called a mermaid's purse © Anke Van Wyk | Dreamstime.com
For oviparous sharks, the eggs are enclosed in small transparent sac-like capsules. These capsules are called « mermaid's purses ».
Did you know?
- There are currently more than 380 species of sharks worldwide !
- The largest fish is a shark: the whale shark, measuring up to 65 feet long !
Discover sharks

Banded houndshark
(Triakis scyllium)
(Triakis scyllium)

Blacknose shark
(Carcharhinus acronotus)
(Carcharhinus acronotus)

Blind shark
(Brachaelurus waddi)
(Brachaelurus waddi)

Copper shark
(Carcharhinus brachyurus)
(Carcharhinus brachyurus)

Dark shyshark
(Haploblepharus pictus)
(Haploblepharus pictus)

Great hammerhead shark
(Sphyrna mokarran)
(Sphyrna mokarran)

Greenland shark
(Somniosus microcephalus)
(Somniosus microcephalus)
Hammerhead shark
(9 espèces)
(9 espèces)

Japanese wobbegong
(Orectolobus japonicus)
(Orectolobus japonicus)

Leafscale gulper shark
(Centrophorus squamosus)
(Centrophorus squamosus)

Lemon shark
(Negaprion brevirostris)
(Negaprion brevirostris)

Oceanic whitetip shark
(Carcharhinus longimanus)
(Carcharhinus longimanus)

Sandbar shark
(Carcharhinus plumbeus)
(Carcharhinus plumbeus)

Silvertip shark
(Carcharhinus albimarginatus)
(Carcharhinus albimarginatus)

Spotted wobbegong
(Orectolobus maculatus)
(Orectolobus maculatus)

Whale shark
(Rhincodon typus)
(Rhincodon typus)
Latest news on sharks
Our latestUpdates

Wednesday, February 18th 2026
The Atlantic tarpon
The Atlantic tarpon is a large coastal fish that can grow up to 8 feet long and weigh over 330 pounds, with a silvery body covered in large, reflective scales. Known as the Silver King, it is famous for its spectacular leaps and fierce fight when hooked by sport fishermen.

Friday, January 30th 2026
The dugong
Discover the dugong, a gentle “sea cow” of tropical waters. Learn about its habitat, diet, reproduction, morphology, and the threats facing this unique marine mammal.

Friday, January 23rd 2026
Dolphins: ocean's smartest creatures
Discover dolphins, the ocean's geniuses: explore their intelligence, social behavior, sophisticated communication, species diversity and vital role in marine ecosystems.
Photo of the Day

Barracuda Méditerranéen
(Sphyraena viridensis)
(Sphyraena viridensis)
